Think about joint tenancy if you buy a property with someone. Let’s break down everything for you to know. You will learn how it works.
You’ll find when the time is right. You will also learn about when to take the necessary risks. Trust me, it’s better to know this ahead of time.
This guide explains joint tenancy, explaining the main features of this form of ownership. It also explains how joint tenancy differs from other types of ownership, and whether it is right for you. Decor
Let’s simplify options for ownership.
Understanding Joint Tenancy Basics
Joint tenancy is a form of shared property ownership where all owners have equal rights and automatic inheritance through survivorship.
What Is Joint Tenancy?

Each person owns the entire property, not just a portion. When you hold property as joint tenants, you all have the same ownership stake. Decor
This differs from sole ownership, where one person owns everything. It also differs from tenancy in common, where owners can have unequal shares and different rights.
Key Characteristics of Joint Tenancy

Equal ownership interests mean everyone owns the same percentage. If three people are joint tenants, each owns one-third.
The four units must exist: time, title, interest, and possession. All owners must acquire their interest at the same time, through the same document, with equal shares, and with equal rights to use the property.
The right of survivorship is the defining feature. When one owner dies, their share automatically goes to the surviving owners. The deceased person’s share doesn’t pass through their will.
How Joint Tenancy Works

Ownership is truly shared among all co-owners. Everyone has equal rights to use and enjoy the entire property. No one can claim a specific part as theirs alone.
When one joint tenant passes away, something automatic happens. Their ownership interest immediately transfers to the surviving joint tenants. The property doesn’t go through probate court.
This transfer happens by operation of law. The surviving owners don’t need to do anything special. They simply continue owning the property, now with fewer owners.
Example Scenario

Sarah and Mike buy a house together as joint tenants. They each own 50% of the property. Both names are on the deed with joint tenancy language.
Years later, Sarah passes away. Mike automatically becomes the sole owner. Sarah’s children don’t inherit her share. Her will doesn’t control what happens to the property. Mike now owns 100% of the house.
Creating a Joint Tenancy

The deed must use explicit wording that creates joint tenancy. Phrases like “as joint tenants with right of survivorship” are common. Vague language won’t work.
All owners must sign the deed at the same time. They must receive their interest from the same transaction.
State laws vary on the details. Some states presume joint tenancy. Others require very specific language. Check your local requirements carefully.
Advantages of Joint Tenancy

Property transfer after death becomes simple. The surviving owners automatically inherit. No court involvement needed.
Avoiding probate saves time and money. Probation can take months and cost thousands. Joint tenancy bypasses this entirely.
Equal control means shared responsibility. All owners have the same rights. Everyone participates in decisions about the property.
Disadvantages and Potential Risks

Inflexibility makes changes difficult. You can’t easily adjust ownership percentages. Selling requires all owners to agree.
One owner’s actions affect everyone. If one person gets sued, the property could be at risk. Bad decisions impact all co-owners.
Creditor exposure creates vulnerability. A creditor can place liens on the property for one owner’s debts. Financial problems spread to everyone.
Loss of control happens at death. Your share automatically goes to co-owners, not your chosen heirs. Your will can’t change this.
How to End or Change a Joint Tenancy

ConvertThink about joint tenancy if you buy a property with someone. Let’s break down everything for you to know. You will learn how it works.
You’ll discover when the time is right. You will also learn about when to take the necessary risks. Trust me, it’s better to know this ahead of time.
This guide explains joint tenancy, explaining the main features of this form of ownership. It also explains how joint tenancy differs from other types of ownership, and whether it is right for you. Decor
Let’s simplify options for ownershiping to tenancy in common is one option. Any owner can do this unilaterally by transferring their interest. This breaks the joint tenancy for that person’s share.
Selling or transferring an ownership share also ends the arrangement. The new owner becomes a tenant in common, not a joint tenant.
Legal actions can force termination. Court orders in divorces or disputes may dissolve the joint tenancy. A partition action can divide the property or force a sale.
Joint Tenancy vs. Other Forms of Ownership
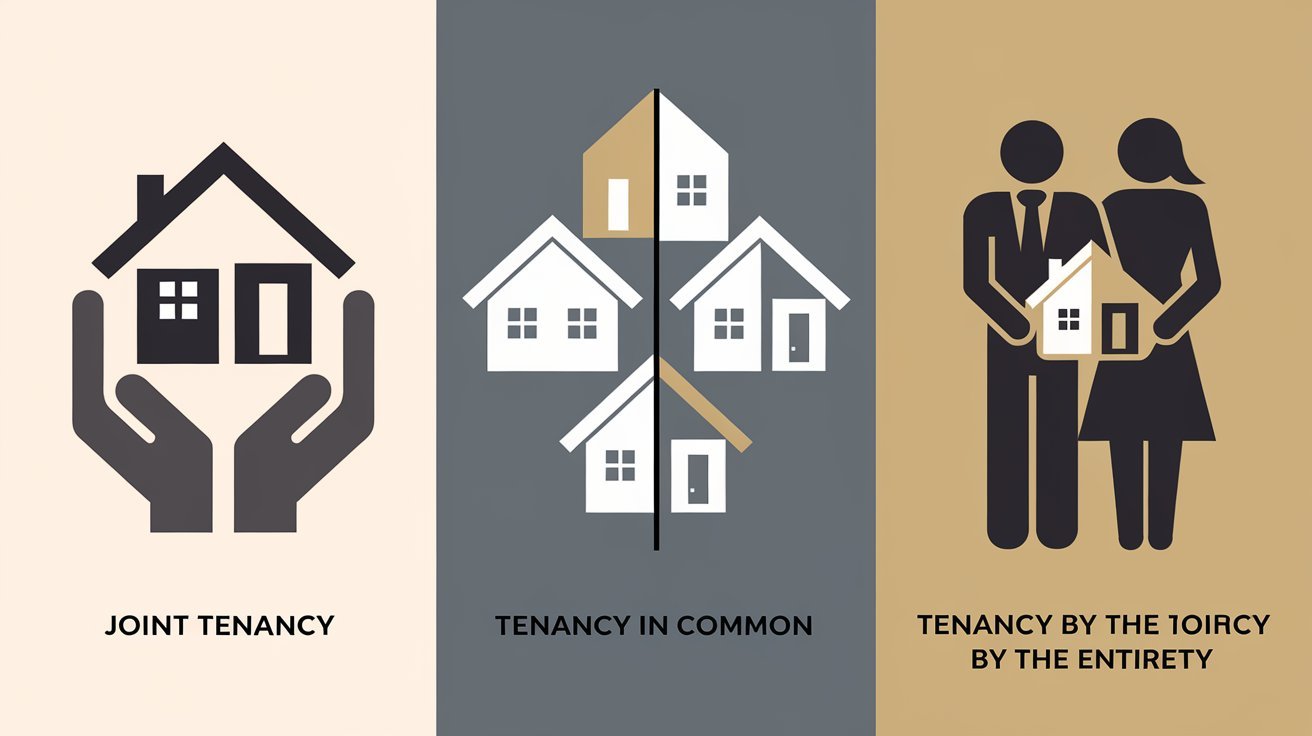
Comparison Table
|
Feature |
Joint Tenancy |
Tenancy in Common |
Tenancy by the Entirety |
|
Ownership Shares |
Must be equal |
Can be unequal |
Must be equal |
|
Right of Survivorship |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Who Can Use It |
Any two or more people |
Any two or more people |
Married couples only |
|
Inheritance |
Goes to surviving owners |
Goes through your will |
Goes to surviving spouse |
|
Selling Your Share |
Breaks the joint tenancy |
Can sell freely |
Both spouses must agree |
|
Creditor Protection |
Limited protection |
No special protection |
Strong protection |
|
State Availability |
All states |
All states |
Limited states |
|
Effect of Divorce |
Remains joint tenancy |
No change |
Converts to tenancy in common |
Legal Implications of Joint Tenancy

Estate planning becomes complicated. Your will can’t control joint tenancy property. This may conflict with your overall estate plan.
Tax considerations matter. The IRS may view the transfer at death as a gift. Capital gains taxes can apply when the property sells. Consult a tax professional about your situation.
Divorce changes everything. Courts often convert joint tenancy to tenancy in common during divorce. Property division follows state divorce laws.
Disputes among co-owners create problems. When owners disagree, legal action may be necessary. Partition lawsuits can force a sale.
When to Consider Joint Tenancy

Ideal situations include married couples. Spouses often use joint tenancy for their family home. The survivor automatically inherits.
Family members sometimes benefit. Parents and children may choose joint tenancy. Siblings inheriting property together might use it.
Alternative structures work better in other cases. Business partners should avoid joint tenancy. People with complex estates need different solutions. If you want control over who inherits, consider other options.
Conclusion
When my cousin and I bought our first rental property together, no one told us property ownership is either joint tenancy, or a few other things. Decor
We found out when we started arguing over things. In hindsight, if I’d just spoken to a lawyer about this, it would have saved us months of problems. Luckily you know what I didn’t. Consult a property lawyer before you make a decision and share this advice with anyone else. Leave a comment if you have questions about your situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I remove someone from joint tenancy without their permission?
No, you cannot remove another owner without their consent. However, you can break the joint tenancy by transferring your own interest to convert your share to tenancy in common.
What happens if one joint tenant wants to sell but others don’t?
The dissenting owner can file a partition lawsuit to force a sale. The court may order the property sold and proceeds divided among all owners.
Does joint tenancy protect property from nursing home costs?
Not necessarily, as transferring property to avoid long-term care costs has serious legal consequences. Many states have look-back periods, so always consult an elder law attorney first.
Can joint tenancy be established through a will?
No, joint tenancy cannot be created through a will and must be established during the owners’ lifetimes. The property deed must specifically state the joint tenancy arrangement when the property is acquired.
How does joint tenancy affect my mortgage?
All joint tenants are typically responsible for the entire mortgage debt. If one person stops paying, lenders can pursue all owners for the full amount owed.